Unlocking the Secrets: Top Treatments for Female Pattern Hair Loss
Why Effective Alopecia Women Treatment Matters More Than Ever
Alopecia women treatment includes a range of medical, procedural, and lifestyle interventions for hair loss. If you're seeing thinning hair or bald spots, you're not alone. About one-third of women experience hair loss, with up to two-thirds of postmenopausal women facing hair thinning. This loss can deeply impact self-confidence and quality of life, as female hair loss is often less socially accepted than male baldness.
Quick Answer: Main Treatment Options for Women
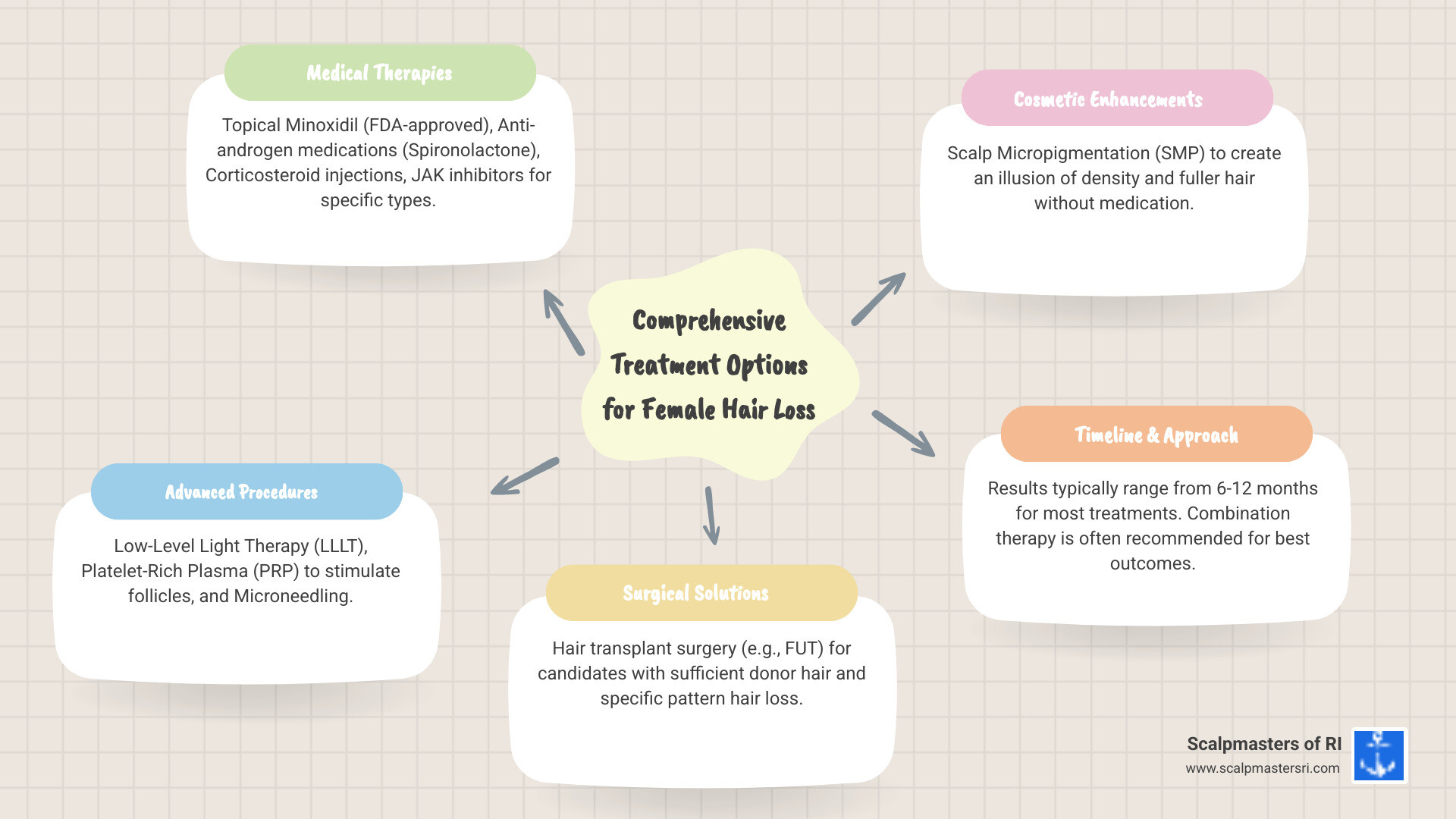
- Topical Minoxidil (Rogaine)- FDA-approved, applied 1-2x daily
- Anti-androgen medications- Spironolactone for hormonal imbalances
- Corticosteroid injections- For patchy alopecia areata (80%+ saw regrowth in studies)
- Low-Level Light Therapy (LLLT)- FDA-approved laser devices
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP)- Stimulates follicles when combined with other treatments
- Hair transplant surgery- For specific candidates with pattern hair loss
- Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP)- Creates the appearance of density without medication
The good news is that modern medicine offers many proven solutions. This guide will walk you through the causes, types, and most effective treatments for female hair loss, from FDA-approved medications to advanced therapies. Understanding your options for conditions like female pattern hair loss, alopecia areata, or stress-related shedding is the first step toward regaining control and confidence.
Understanding Female Hair Loss: Causes, Types, and Diagnosis
Hair loss in women is complex, influenced by genetics, hormones, and environmental factors. Identifying the root cause is the first step toward effective alopecia women treatment.
Common Causes and Types of Female Hair Loss
-
Androgenetic Alopecia (Female Pattern Hair Loss - FPHL): The most common type, FPHL is often inherited and linked to androgens (male hormones). Unlike men, women typically see gradual thinning at the part line and diffuse loss from the top of the head, while the hairline rarely recedes. The hair's growing phase shortens, and follicles shrink, replacing thick hairs with thinner ones. FPHL is common, affecting about two-thirds of postmenopausal women. Its severity is often described using the Ludwig Classification (Type I, II, III).
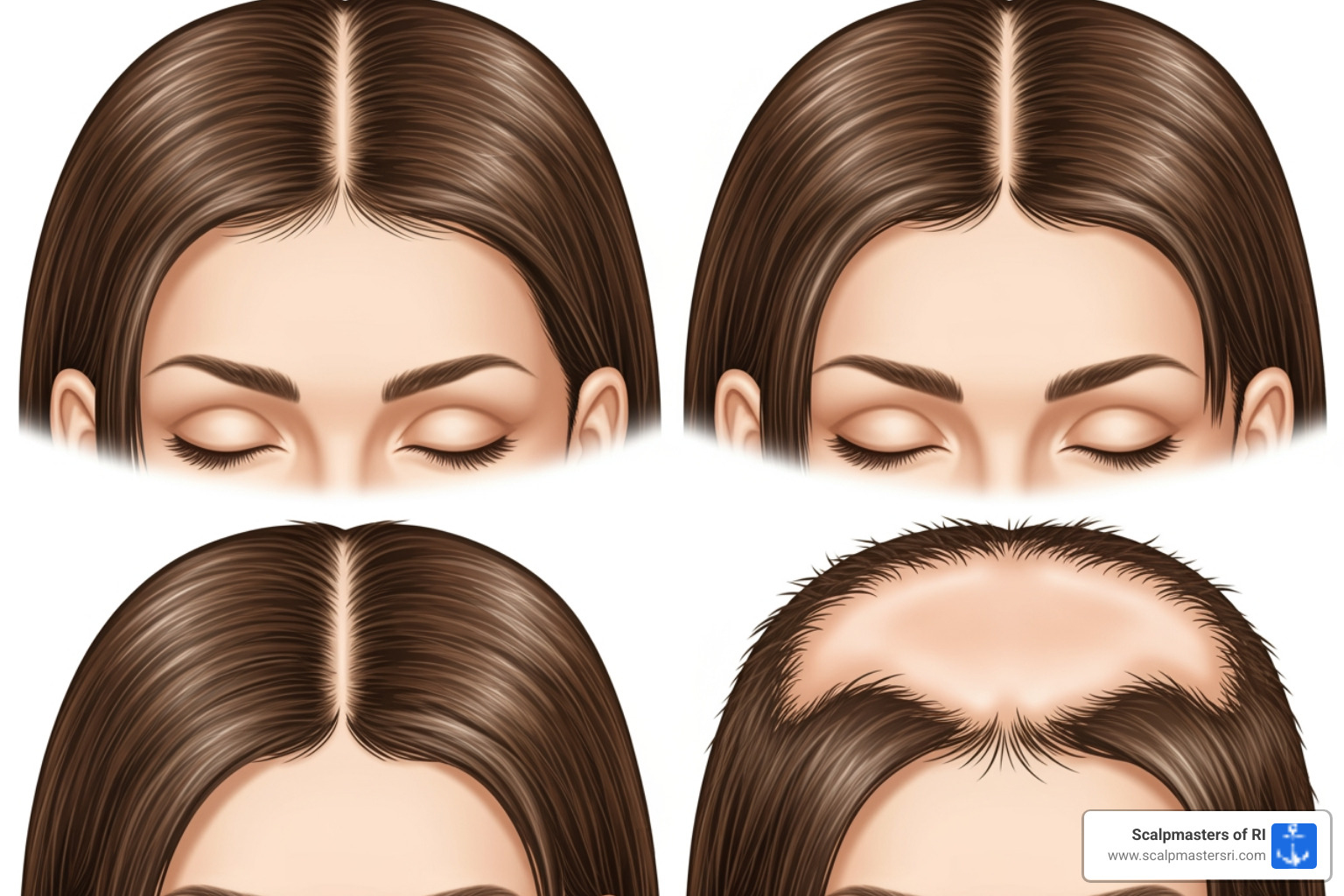

-
Telogen Effluvium: This type of shedding occurs after a significant stressor like major surgery, childbirth, severe illness, or drastic weight loss. It pushes many hair follicles into the resting (telogen) phase, causing excessive shedding months later. This condition often resolves on its own once the underlying cause is addressed.
-
Alopecia Areata: An autoimmune condition where the body attacks its own hair follicles, causing patchy hair loss. In severe cases, it can lead to total hair loss on the scalp (alopecia totalis) or body (alopecia universalis).
Hormonal Factors: A Key Influence
Hormonal imbalances often trigger or worsen hair loss.
- PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome): Higher androgen levels in women with PCOS can cause thinning hair on the scalp.
- Menopause: Declining estrogen and progesterone levels can increase the relative influence of androgens, leading to diffuse hair thinning.
- Post-Pregnancy: A sudden drop in estrogen after childbirth can cause temporary but significant shedding (a form of telogen effluvium).
Other Contributing Factors
- Stress: Chronic stress can increase shedding.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Low levels of iron, zinc, and vitamin D can impact hair growth.
- Genetics: Genes play a major role, especially in androgenetic alopecia.
- Medical Conditions and Medications: Thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases, and certain drugs can cause hair loss.
When to Seek Professional Advice
If you notice unusual shedding or thinning, see a professional. A dermatologist can diagnose the issue and recommend treatments. The diagnostic process may include:
- A physical exam and review of your medical history, diet, and hair care routine.
- Blood Tests: To check for underlying conditions like thyroid issues or nutritional deficiencies.
- Pull Test: Gently pulling hair to see how many strands come out.
- Scalp Biopsy: Examining a small skin sample to confirm the diagnosis.
- Trichoscopy: Using a dermatoscope for a close-up view of the scalp and hair.
- Hormonal Evaluation: To check hormone levels if an imbalance is suspected.
As the Mayo Clinic notes, a thorough exam and history are key to diagnosis. Explore Mayo Clinic studies Diagnosis to learn more.
Medical Alopecia Women Treatment: Medications and Prescriptions
Once your hair loss is diagnosed, your doctor can recommend medical treatments to slow hair loss, stimulate regrowth, or address hormonal issues.
Primary Medical Treatments
-
Minoxidil (Rogaine): The most recognized alopecia women treatment, Minoxidil is FDA-approved for female pattern hair loss (FPHL) and is available over-the-counter (2% or 5% solutions/foam).
- Topical Minoxidil: Applied to the scalp once daily, it stimulates hair growth. It takes at least six months to see results, and continuous use is required to maintain them. Side effects can include scalp irritation and unwanted hair growth in other areas.
- Oral Minoxidil: Low-dose oral minoxidil is gaining popularity as a convenient off-label alternative.
-
Anti-androgen Medications: These are effective when excess androgens contribute to hair loss.
- Spironolactone (Aldactone): This medication slows androgen production and blocks them from affecting hair follicles. It's often prescribed for conditions like PCOS and may be combined with oral contraceptives.
- Finasteride (Propecia/Proscar): Primarily for male pattern baldness, Finasteride is sometimes prescribed off-label for post-menopausal women. Crucially, women who are pregnant or may become pregnant must not take or handle this drug due to the risk of birth defects.
- Other Anti-androgens: Dutasteride and Bicalutamide are other options used in specific cases of hyperandrogenism.
-
Corticosteroid Injections: For patchy hair loss from alopecia areata, injecting corticosteroids directly into the scalp is a common and effective treatment. Studies show over 80% of patients had significant regrowth within 12 weeks. For more extensive cases, oral medications like prednisone may be used to suppress the immune system.
-
JAK Inhibitors: These are a newer class of medications for severe alopecia areata. Drugs like Baricitinib and Ritlecitinib calm the overactive immune system, preventing it from attacking hair follicles. Studies show these can lead to 50% or greater hair regrowth.
Treatment Approach for Different Alopecia Types
- Female Pattern Hair Loss (FPHL): Treatment typically involves topical minoxidil and/or anti-androgen medications. Early treatment is key, as prolonged FPHL can destroy hair follicles.
- Alopecia Areata: The goal is to stop the immune attack. This may involve corticosteroids, contact immunotherapy, or newer JAK inhibitors.
No single treatment works for everyone. Learn more about the broader landscape of treatments in More info about the hair loss industry.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
All medical treatments have potential side effects. Discuss these with your doctor.
- Minoxidil: Requires indefinite use to maintain results.
- Anti-androgens: Require regular monitoring for side effects like changes in potassium levels with spironolactone.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Many hair loss medications, especially Finasteride, are not safe during pregnancy or breastfeeding. Always inform your doctor of your plans.
Advanced, Procedural, and Complementary Therapies
Beyond daily medications, several advanced procedures and complementary therapies offer hope for women with hair loss, often used with medical treatments for better results.
Procedural Treatments
- Hair Transplant Surgery: This surgical option involves moving hair follicles from a dense donor area (like the back of the scalp) to thinning areas. The most common technique is Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT). It's an option for patients with stable hair loss patterns but isn't suitable for everyone, especially those with widespread thinning. Risks include bleeding, swelling, and infection, and multiple surgeries may be needed.
- Low-Level Light Therapy (LLLT): This non-invasive treatment uses FDA-approved medical-grade lasers or LED devices to stimulate hair follicles, reduce inflammation, and increase blood flow to the scalp.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): PRP therapy uses injections of your own concentrated blood platelets to stimulate hair follicles. It is most effective when combined with other hair growth treatments.
- Microneedling: This technique uses a device with tiny needles to create micro-injuries in the scalp, which is thought to stimulate collagen and improve blood flow. It's often used with topical treatments like minoxidil to improve their absorption.
For a detailed comparison of procedural options, read Comparing Scalp Micropigmentation to Hair Transplants.
Complementary Alopecia Women Treatment: Beyond Medication
Sometimes, the goal is creating the appearance of fuller hair. This is where cosmetic solutions excel.
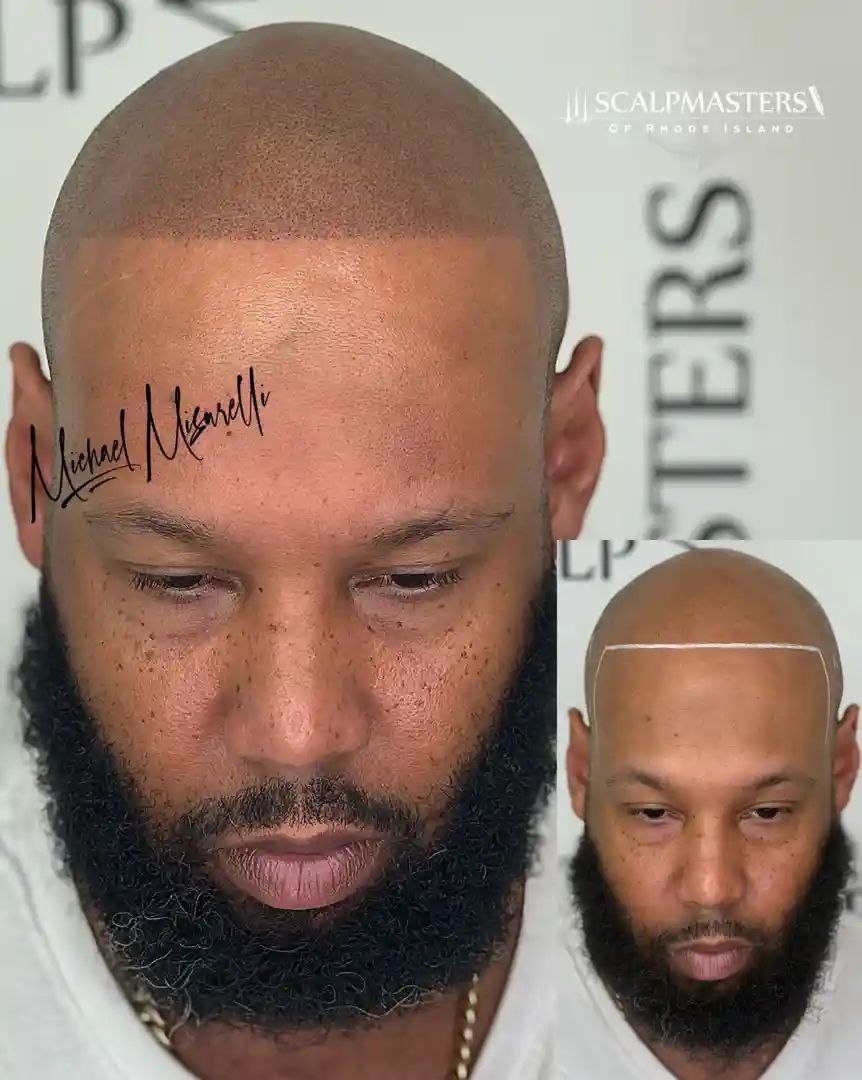
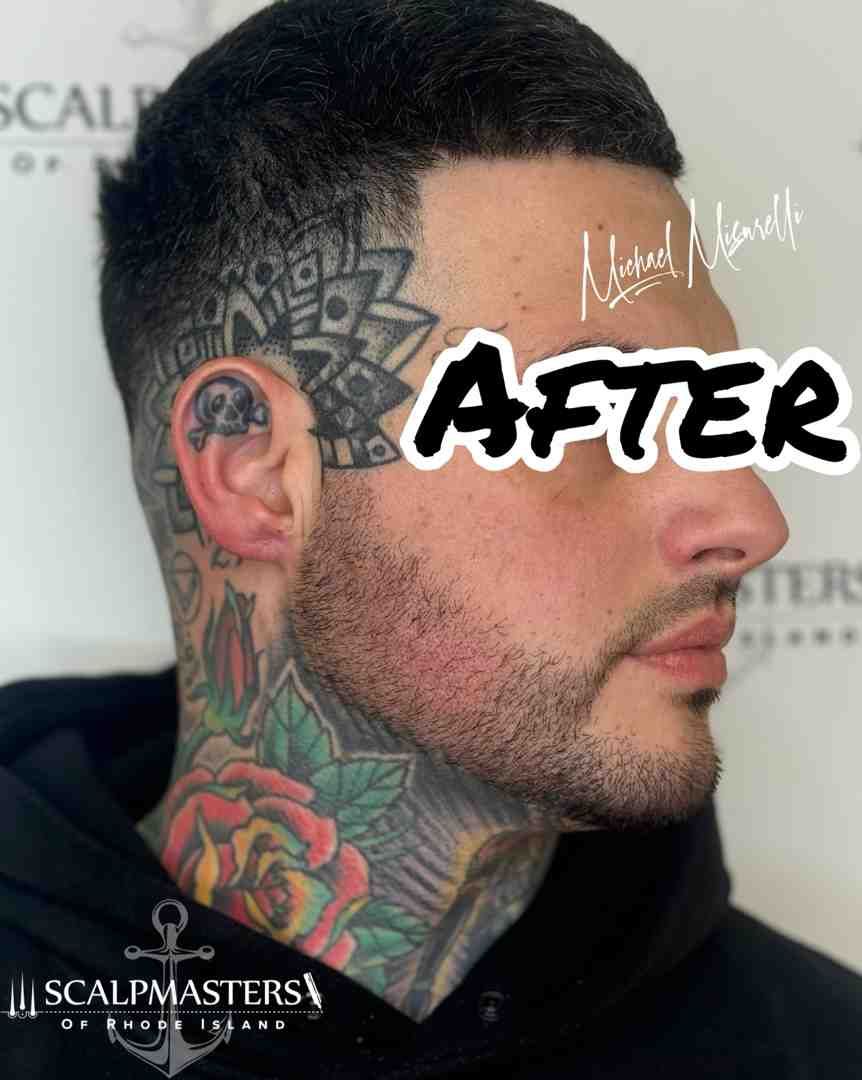
Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP)
Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP) is a revolutionary, non-surgical alopecia women treatment that creates the illusion of thicker hair. At Scalpmasters of RI, based in Cranston, Rhode Island, we specialize in this technique, helping women across New England, including Massachusetts and Connecticut, regain their confidence.
- Creating Density Illusion: Our skilled practitioners use micro-needles to deposit natural pigments onto the scalp. These tiny dots replicate hair follicles, reducing the contrast between your scalp and hair for an immediate look of increased density.
- Non-Invasive Solution: Unlike surgery, SMP is non-invasive with no downtime. It's a great alternative for those who aren't candidates for medical or surgical options or who want immediate cosmetic improvement.
- Ideal Candidates for SMP: SMP is ideal for women with diffuse thinning, a widening part, or alopecia who want to camouflage bald spots. It's also excellent for adding perceived density after a hair transplant. Our approach at Scalpmasters of RI is customized for the unique patterns of female hair loss. Learn how we help women at Scalp Micropigmentation for Women.
- Long-Lasting Results: SMP offers long-lasting results, typically needing touch-ups every few years. To understand the process, explore How Scalp Micropigmentation Works. Our founder’s artistry ensures natural-looking results that restore confidence.
Lifestyle, Nutrition, and At-Home Management
While medical and procedural treatments are powerful, your daily habits also have a significant impact. Lifestyle, nutrition, and gentle hair care are a crucial foundation for managing hair loss.
Balanced Diet and Key Nutrients
A balanced diet supports hair growth and strength. Key nutrients include:
- Iron: Iron deficiency can contribute to hair loss, especially for vegetarians or women with heavy periods.
- Zinc: Essential for hair tissue growth and repair.
- Vitamin D: Research links vitamin D deficiency to hair loss.
- Biotin: Vital for hair health, though deficiencies are rare with a balanced diet.
- Protein Intake: Hair is mostly protein, so sufficient intake is crucial for strong strands. Wondering, Can Lack of Protein Cause Hair Loss? Yes, it can.
Consult your healthcare provider before taking supplements. For more on this topic, see Vitamins and supplements for hair.
Gentle Hair Care Practices
Your hair care routine can cause damage. Adopting a gentle approach is vital.
- Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Be mindful of ingredients in hair products. Some treatments contain harmful chemicals that can lead to shedding.
- Reduce Heat Styling: Excessive heat from blow dryers and flat irons can cause breakage. Air-dry when possible or use a heat protectant.
- Gentle Handling: Avoid tight hairstyles that pull on follicles (traction alopecia). Use a wide-toothed comb on wet hair.
- Scalp Health: A healthy scalp is key. Regular, gentle cleansing and massage can improve circulation.
Stress Management Techniques
Since stress can trigger hair loss, incorporating stress-reduction techniques can make a real difference.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: These practices can help calm your nervous system.
- Yoga and Exercise: Physical activity is a great stress reliever.
- Adequate Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep.
- Professional Support: Consider talking with a mental health professional to manage stress.
The Emotional Journey: Coping with Hair Loss
Hair loss is more than a physical condition; it deeply affects a woman's emotional well-being, often leading to decreased self-esteem, social anxiety, and feelings of helplessness.
Coping Strategies and Support
Navigating the emotional side of hair loss requires a multi-faceted approach.
- Seek Support Groups: Connecting with others who share your experience can reduce feelings of isolation.
- Consider Counseling: A mental health professional can provide tools for coping with the emotional distress that may accompany hair loss.
- Explore Camouflage Techniques:
Visually improving your hair's appearance can significantly boost confidence.
- Wigs and Hairpieces: Modern wigs are natural-looking and offer a versatile solution.
- Styling for Volume: Certain haircuts and styling techniques can create the illusion of fuller hair.
- Hair Thickening Products: These products temporarily coat hair shafts to make them appear fuller.
- Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP): As discussed, SMP creates a density illusion, making thinning less noticeable.
- Building Confidence: Focus on building confidence from within by engaging in hobbies you love or practicing self-compassion.
For a deeper dive into the emotional aspects, read Exploring the emotional impact and support resources. You are not alone on this journey.
Frequently Asked Questions about Female Hair Loss
We often hear common questions from women concerned about hair loss. Here are some of the most frequent ones:
How long do hair loss treatments for women take to work?
Patience and consistency are key, as timelines vary by alopecia women treatment.
- Minoxidil: It typically takes at least six months of consistent daily use to see results, with more significant improvement around 8-12 months.
- Anti-androgen Medications: These can also take 3-6 months to show visible effects.
- Corticosteroid Injections: For alopecia areata, regrowth can appear within 12 weeks.
- Procedural Treatments (PRP, LLLT): These usually require multiple sessions over several months, with results appearing after 3-6 months.
- Hair Transplant Surgery: Final results are visible around 12-18 months after the procedure.
- Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP): This cosmetic solution offers an immediate visual improvement in density after your sessions.
Is female hair loss reversible?
This depends entirely on the underlying cause.
- Often Reversible: Hair loss from temporary conditions like stress, illness, or post-pregnancy shedding (telogen effluvium) is often reversible once the trigger is gone.
- Manageable, Not Curable: Androgenetic alopecia (female pattern hair loss) is a progressive condition. Treatments can slow loss and promote regrowth but must be continued indefinitely to maintain results.
- Variable Outcome: Alopecia areata can be unpredictable. Hair may regrow on its own or with treatment, but the condition can be recurrent.
Early diagnosis is crucial to preserve hair follicles and maximize the potential for regrowth.
What is the most effective treatment for female pattern hair loss?
There is no single "most effective" alopecia women treatment for everyone. The best approach is personalized.
- Minoxidil is the only FDA-approved topical treatment: For female pattern hair loss (FPHL), topical minoxidil (2% or 5%) is the only FDA-approved over-the-counter solution and is often a first-line treatment.
- Combination Therapy is Common: The most effective strategy often combines treatments, such as using topical minoxidil with an oral anti-androgen like spironolactone.
- Custom Approach: A dermatologist can create a personalized plan based on your specific diagnosis, medical history, and lifestyle.
- Addressing Underlying Causes: If hair loss is caused by a medical condition or nutritional deficiency, treating that underlying issue is the most effective step.
The "best" treatment is the one that is most effective and sustainable for you , under professional guidance.
Conclusion: Finding Your Path to Confidence
Navigating alopecia women treatment can feel overwhelming, but many paths are available. We've covered the diverse causes of female hair loss and a comprehensive array of solutions, from FDA-approved medications like minoxidil to advanced therapies like PRP and hair transplantation. We've also highlighted the importance of lifestyle, nutrition, and emotional support.
The most vital step is getting a professional diagnosis. Consulting a dermatologist or hair loss specialist in Rhode Island, Massachusetts, or Connecticut is crucial for developing a personalized treatment plan.
At Scalpmasters of RI, we believe in empowering women through effective solutions. While we specialize in non-invasive cosmetic options like Scalp Micropigmentation, we are dedicated to helping you find the right path to restore not just the appearance of fuller hair, but also your confidence.
Ready to take the next step? Discover how Scalp Micropigmentation can restore the look of fuller hair for women and schedule a consultation with our experts today.
Learn More
What's New
Latest Hair Loss Solutions & Guides




